Common Name
Silver maple
Plant Form
Large Trees
Duration
Perennial
Max Height (ft)
80.0
Width (ft)
40.0 -
60.0
Growth Rate
Fast
Region
Coastal
Piedmont
Mountain
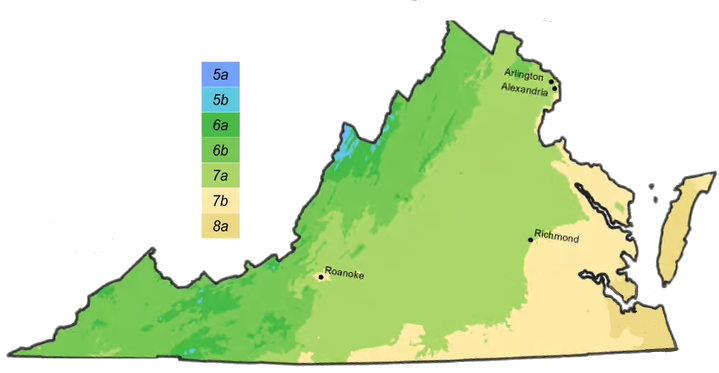
Hardiness Zone
5,
6,
7,
8,
9
Commercially available
Yes
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF):
Additional Info
Habitat: Well-drained floodplain forests, riverbanks, large-river backswamps, and sand, gravel, and rocky bar woodlands; also frequently cultivated and escaped into weedy upland and alluvial habitats. Locally common in the mountains and the northern Piedmont and inner part of the northern Coastal Plain from the James River north; infrequent elsewhere.
Wildlife Value: Members of the genus Acer support Imperial Moth (Eacles imperialis) larvae. Adult Imperial Moths do not feed. Early spring source of nectar for bees. Seeds are eaten by squirrels, chipmunks and birds. Buds are eaten by squirrels after the seeds have sprouted.
Edibility: Sap can be used to make syrup
Notes: The wood is weak and breaks easily in storms and with snow loads.
Flower Color
Red/burgandy
Gold/Yellow
Green
Flower Prominence
Reduced
Bloom Time
Spring
Bloom Month
February
March
April
Fall Color
Brown/Copper
Gold/Yellow
Light Requirements
Full sun
Partial sun
Moisture Requirements
Moist
Soil Texture
Shallow rocky
Seed or Fruit eaten by wildlife?
Yes
Pollinators
Bees
Butterfiles
Top 30 for Butterfly and Moth Caterpillars?
Yes
Number of Lepidotera Species Genus Supports
285
Nurseries that may carry live plant


